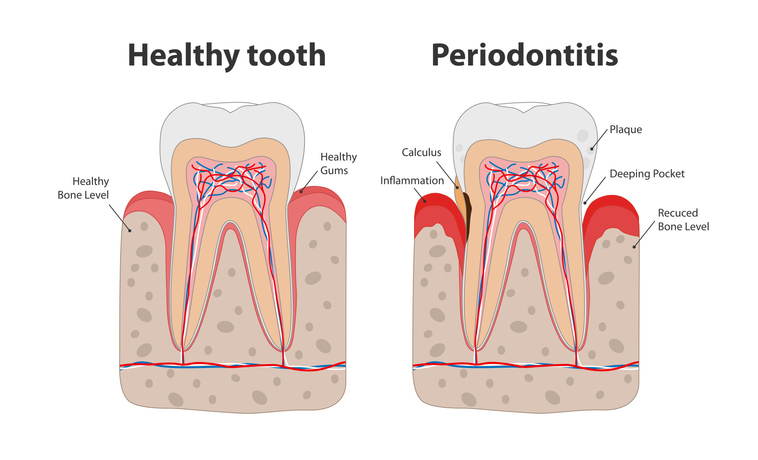
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but serious condition that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. It ranges from simple gum inflammation, known as gingivitis, to more severe conditions like periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated. Understanding gum disease is crucial for maintaining oral and overall health.
Overview of Gum Disease
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These pockets collect debris and can become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen, and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. This can lead to loose teeth and eventual tooth loss.
Importance of Oral Health
Oral health is a window to your overall health. Conditions in the mouth can affect the rest of the body. For instance, bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, potentially causing heart disease, respiratory issues, and complications in diabetes. Maintaining healthy gums is essential not just for a bright smile but also for your overall well-being.
Prevalence
Gum disease is more common than many realize. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly half of adults aged 30 and older have some form of periodontal disease. The prevalence increases with age, with over 70% of adults aged 65 and older affected. These statistics highlight the importance of regular dental checkups and proper oral hygiene to prevent and manage gum disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of gum disease can help you take proactive steps to protect your oral health.
Common Causes
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque buildup. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If not removed through daily brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Other common causes include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gum disease.
- Genetic factors: Some individuals are more prone to gum disease due to genetic predisposition.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of developing gum disease:
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Diet: Poor nutrition can weaken the immune system and contribute to gum disease.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes can increase susceptibility to infections, including gum disease.
- Medications: Certain medications can reduce saliva flow, leading to dry mouth and increasing the risk of gum disease.
Warning Signs
Early detection of gum disease is crucial for effective treatment. Watch for these warning signs:
- Bleeding gums: Gums that bleed during and after brushing.
- Bad breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Gum recession: Gums that are pulling away from the teeth, causing them to look longer.
- Loose teeth: Teeth that are shifting or becoming loose.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to visit a periodontist for an evaluation.
Home Care Strategies
Preventing and managing gum disease starts with good oral hygiene at home. Here are some effective strategies:
Daily Oral Hygiene Routine
A consistent oral hygiene routine is the first line of defense against gum disease. Here’s what you should do daily:
- Brush twice a day: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Brush for at least two minutes, ensuring you clean all surfaces of your teeth.
- Floss daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between the teeth and under the gumline, areas where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Use mouthwash: An antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
Diet and Nutrition
Your diet plays a significant role in your oral health. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, are beneficial for gum health. Incorporate the following into your diet:
- Fruits and vegetables: High in vitamins and antioxidants.
- Dairy products: Good sources of calcium and vitamin D.
- Lean proteins: Help repair tissue.
Avoid sugary and acidic foods and drinks, as they can contribute to plaque buildup.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact your oral health:
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease. Quitting can improve your gum health and overall well-being.
- Reduce stress: High stress levels can weaken the immune system and make it harder to fight off infections, including gum disease.
- Manage medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes should be well-controlled to reduce the risk of gum disease.
Taking these steps can help you maintain healthy gums and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Professional Treatments
While home care is essential, professional dental treatments are crucial for managing and treating gum disease, especially in its more advanced stages.
Regular Dental Checkups
Biannual visits to your dental team are vital for maintaining healthy gums. During these visits, your dentist will:
- Conduct thorough cleanings: Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that regular brushing and flossing can’t.
- Perform examinations: Regular checkups help detect early signs of gum disease and other oral health issues.
- Provide personalized advice: Your dentist can offer tips and recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
Deep Cleaning Procedures
If you have signs of gum disease, your dentist may recommend deep cleaning procedures like scaling and root planing. These treatments go beyond regular cleanings to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooth the root surfaces, helping gums reattach to the teeth.
Advanced Treatments
For more severe cases of gum disease, additional treatments may be necessary:
- Antibiotic therapy: Antibiotics can be used to control bacterial infection. They come in various forms, such as mouthwash, gel, or oral medication.
- Laser treatment: Lasers can be used to remove infected tissue and promote the healing of the gums.
- Surgical procedures: In advanced cases, surgical treatments like flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be required to restore supportive tissues.
These professional treatments, combined with diligent home care, can effectively manage and even reverse gum disease.
Preventive Measures and Long-term Care
Preventing gum disease and maintaining oral health requires ongoing effort and attention. Here are some long-term strategies to keep your gums healthy.
Maintaining Oral Hygiene
Consistently following a good oral hygiene routine is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Brush and floss regularly: Stick to brushing twice a day and flossing daily.
- Use the right tools: Consider using an electric toothbrush and interdental brushes for more effective cleaning.
- Rinse with mouthwash: Antimicrobial mouthwash can help keep bacteria at bay.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your oral health is essential to catch any issues early. Here’s what you can do:
- Schedule regular dental visits: Keep up with biannual checkups and cleanings.
- Self-examine your mouth: Look for signs of gum disease, such as bleeding, swelling, or recession, and report any concerns to your dentist.
- Stay informed: Keep yourself updated with the latest recommendations and advancements in oral health care.
Future Research and Innovations
The field of dentistry is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and new technologies improving the way we prevent and treat gum disease. Some potential future treatments include:
- Regenerative therapies: Techniques to regenerate lost bone and gum tissue.
- Advanced antimicrobial treatments: New medications and formulations to better target harmful bacteria.
- Genetic testing: Personalized treatments based on genetic susceptibility to gum disease.
Staying informed about these advancements can help you make proactive decisions about your oral health care.
Final Thoughts on Managing Gum Disease
Managing gum disease requires a combination of diligent home care and professional treatments. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following a comprehensive care routine, you can effectively prevent and manage gum disease. Remember, maintaining healthy gums is not just about preserving your smile; it’s about protecting your overall health.
At Periodontal Associates of Memphis, our team is dedicated to helping you achieve and maintain optimal oral health. If you have any concerns about your gum health or need professional care, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with us. Together, we can ensure your gums stay healthy and your smile stays bright.
